A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners (From Zero to Deployment)
Introduction: Your Journey Starts Here
Becoming a full stack developer may sound overwhelming at first, especially if you are new to programming. You might be asking yourself questions like:
- Where do I start?
- Which technologies should I learn first?
- How long will it take?
- Do I need a computer science degree?
The good news is this: you do not need to know everything from day one. Thousands of successful full stack developers today started exactly where you are now — with curiosity, patience, and consistency.
This guide is written for fresh software developers and complete beginners who want a clear, practical, step-by-step roadmap. By the end of this journey, you will understand how websites work, how to build them from scratch, and how to deploy a real website online.
This article is written in simple, human language, not technical jargon, so you can easily follow along and grow with confidence.
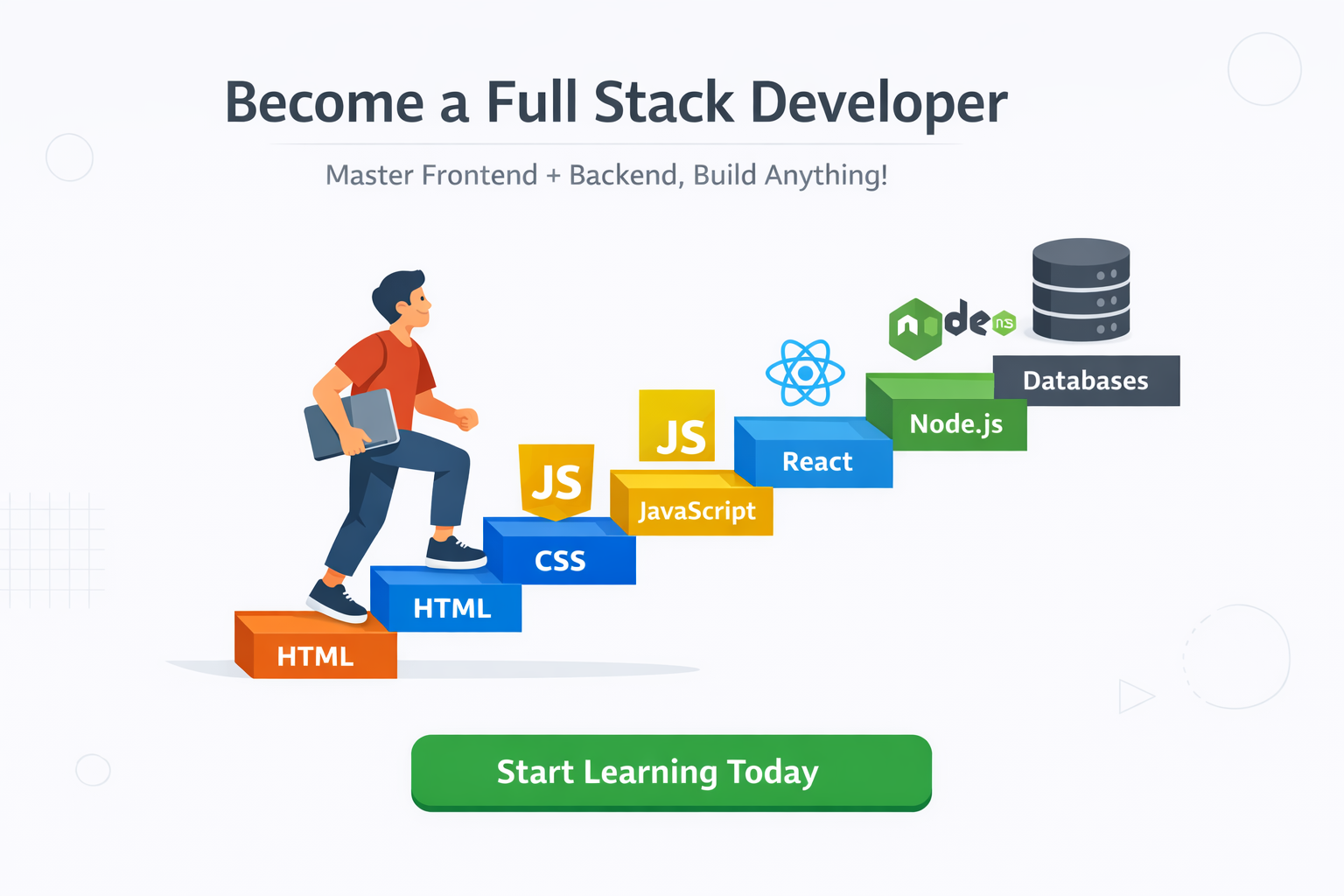
What Is a Full Stack Developer?
Before jumping into the learning path, let’s clearly understand what a full stack developer actually does.
A full stack developer is someone who can work on:
- Frontend – what users see and interact with
- Backend – how data is processed and stored
- Database – where information lives
- Deployment – how the website goes live on the internet
Think of a website like a restaurant:
- Frontend is the dining area (what customers see)
- Backend is the kitchen (where work happens)
- Database is the storage room
- Deployment is opening the restaurant to the public
As a full stack developer, you understand the entire system, even if you later specialize in one area.
Step 1: Learn How the Internet and Websites Work (Very Important)
Most beginners skip this step, but this is one of the most important foundations.
Before writing code, you should understand how websites actually work.
Basic Concepts You Must Understand
Take time to learn these concepts first:
- What is a website?
- What is a browser?
- What is a server?
- What is a domain name?
- What is hosting?
- What happens when you type a website URL?
When someone visits a website:
- The browser sends a request
- The server processes the request
- The server sends back data
- The browser displays the page
You don’t need deep technical details yet — just how everything connects.
Why This Step Matters
Understanding this early will:
- Make learning easier later
- Reduce confusion
- Help you debug problems faster
- Make you feel confident, not lost
Step 2: Start with Frontend Development (Your First Real Code)
Frontend development is the best place for beginners to start, because you can see results immediately.
Frontend development focuses on what users see on the screen.
The 3 Core Frontend Technologies
Every website uses these three technologies:
1. HTML – The Structure
HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language.
HTML is like the skeleton of a website. It defines:
- Headings
- Paragraphs
- Images
- Links
- Forms
- Buttons
HTML is not programming — it’s markup — and it’s very beginner-friendly.
You should learn:
- HTML tags
- Page structure
- Forms and inputs
- Semantic HTML (important for SEO and AdSense)
2. CSS – The Design
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets.
CSS controls:
- Colors
- Fonts
- Layout
- Spacing
- Responsiveness
Without CSS, websites look plain and boring.
You should learn:
- Flexbox
- Grid
- Responsive design
- Mobile-first layouts
This is extremely important for AdSense approval because Google prefers clean, responsive websites.
3. JavaScript – The Interaction
JavaScript makes websites interactive.
It allows you to:
- Handle clicks
- Validate forms
- Create animations
- Load content dynamically
At first, JavaScript may feel difficult — this is normal.
Start with:
- Variables
- Functions
- Loops
- Events
- DOM manipulation
Step 3: Build Small Frontend Projects (Practice Is Everything)
Learning without building is like reading about swimming without entering water.
You should build small projects such as:
- Personal portfolio
- Landing page
- Simple blog layout
- Contact form
- To-do list
These projects will:
- Improve confidence
- Teach real-world problem solving
- Prepare you for backend development
Do not aim for perfection. Aim for progress.
Step 4: Learn Version Control (Git and GitHub)
Once you start coding regularly, you must learn version control.
What Is Git?
Git helps you:
- Save your code history
- Undo mistakes
- Work on features safely
What Is GitHub?
GitHub is a platform to:
- Store your code online
- Share projects
- Build a developer profile
- Collaborate with others
You should learn:
- Git init
- Git add
- Git commit
- Git push
- Git pull
This skill is mandatory for professional developers.
Step 5: Understand Backend Development (The Brain of the Website)
Now that you are comfortable with frontend basics, it’s time to move to backend development.
Backend handles:
- User authentication
- Business logic
- Data processing
- API communication
Choosing a Backend Language
Popular backend options include:
- JavaScript (Node.js)
- Python
- PHP
- Java
For beginners, Node.js is a great choice because:
- You already know JavaScript
- One language for frontend and backend
- Large community support
Step 6: Learn Backend Basics with Node.js
When learning backend, focus on fundamentals:
- How servers work
- Handling requests and responses
- Creating APIs
- Managing routes
- Error handling
You should also learn Express.js, a popular Node.js framework that simplifies backend development.
Step 7: Learn Databases (Where Data Lives)
Every real website uses a database.
Databases store:
- User data
- Posts
- Comments
- Products
- Settings
Types of Databases
You should understand:
- SQL databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL)
- NoSQL databases (MongoDB)
For beginners, MongoDB is easy to start with.
Learn:
- CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete)
- Data modeling
- Relationships
Step 8: Connect Frontend, Backend, and Database
This is where everything comes together.
You will learn how to:
- Send data from frontend to backend
- Store data in database
- Fetch data back to frontend
- Handle errors properly
This step turns you into a real full stack developer, not just a learner.
At this point, we have covered:
- Web fundamentals
- Frontend development
- Git and GitHub
- Backend basics
- Databases
👉 Next sections will cover:
- Authentication (login & signup)
- Security best practices
- Project structure
- Testing
- Deployment (from local to live website)
- SEO basics for AdSense
- Mistakes beginners should avoid
- Final roadmap and learning timeline
🚨 Common Pitfalls to Avoid:
- Tutorial hell – Build your own projects as soon as possible
- Trying to learn everything – Focus on one stack first
- Skipping fundamentals – You’ll pay for it later
- Not deploying early – Deploy even small projects to get comfortable
- Comparing yourself – Everyone learns at their own pace
Remember, the first website you deploy won’t be perfect. Mine looked terrible! But hitting that “deploy” button for the first time is an amazing feeling.
Start small, be consistent, and don’t be afraid to break things. You’ll have moments of frustration followed by moments of “AHA!” that make it all worth it.
You got this! When you launch your site, come back and share the link – I’d love to see what you build. 🚀