Laravel full guide step by step
MVC stands for:
M – Model
V – View
C – Controller
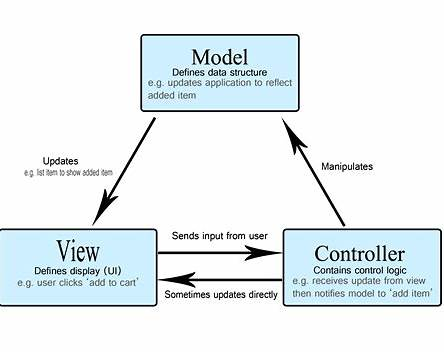
It’s an architectural pattern used by Laravel (and many other frameworks) to organize your code in a clean and maintainable ways.
The Three Pillars of MVC
1. Model — Your Data Brain
The main logic of the database
It mainly Deals with your database and business logic.
The Model represents your database tables.
In Laravel, Models are usually stored in the app/Models folder.
They handle things like:
Fetching data from the database
Saving new records
Updating and deleting records
Defining relationships (e.g. A single user can have many posts)
Example:
// app/Models/User.php
class User extends Model
{
protected $fillable = ['name', 'email', 'password'];
}
Here, the User model talks to the users table in your database.
It’s like the bridge between your code and your data.
2. View — The User Interface
The mainly focus on Shows the data to the user (UI).
Views are stored in resources/views.
They are basically Blade template files (Laravel’s HTML + PHP mix).
Views should not have heavy logic
- just show data given by the Controller.
Example
<!-- resources/views/users.blade.php -->
<h1>All Users</h1>
<ul>
@foreach ($users as $user)
<li>{{ $user->name }}</li>
@endforeach
</ul>
This is what your users actually see in the browser.
3. Controller The middle man
Mainly focus onConnecting Models and Views.
Controllers’ stores in app/Http/Controllers.
They receive HTTP requests (like visiting a page, submitting a form),
talk to the Model, and then return the proper View with data.
Example:
// app/Http/Controllers/UserController.php
class UserController extends Controller
{
public function index() {
$users = User::all(); // talk to the model and display all user from database
return view('users', compact('users')); // pass data to view
}
}
Here, the Controller is the middleman: it asks the Model for all users and gives them to the View to display.
How the MVC Flow Works in Laravel
Let’s imagine a real-life user visiting http://127.0.0.1:8000/users
User hits a route
Laravel looks at routes/web.php
Route::get(‘/users’, [UserController::class, ‘index’]);
Route calls a Controller method → UserController@index
Controller talks to the Model → User::all() // select all user from database and display to the users
Model gets data from the database
Controller sends the data to a View
- return view(‘users’, compact(‘users’))
View displays the data as HTML in the browser
Your user sees a clean web page, but behind the scenes, MVC kept everything organized and separated.
Why MVC Is So Helpful
Organized/ modularize code – Each part does only one job/ each module works only one jobs for its works only. Mainly focus on separation of concern on logic and views.
Reusable & scalable – You can add new features easily without breaking everything.
Team-friendly –
- Frontend devs can work on Views,
- backend devs on Models/Controllers.
Imagine a team where one person builds the house structure
- (Model),
- One decorates it (View),
- One directs who does what (Controller).
- That’s how smooth MVC makes development.
Practice Challenge
Let’s now build a complete CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) system in Laravel
We’ll build a Student Management CRUD as an example.
Step 1 Create a Fresh Laravel Project
- composer create-project laravel/laravel sms
- cd student-crud
- php artisan serve
Open http://localhost:8000 to see fresh the Laravel welcome page.
Step 2 Connect to Database/ Database configuration
Create a database named sms_db in MySQL
Update your .env file:
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
DB_HOST=127.0.0.1
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE=sms_db // your database
DB_USERNAME=root
DB_PASSWORD=
Step 3 Create Student Model & Migration
php artisan make:model Student -mThis provides:
app/Models/Student.phpdatabase/migrations/2025-0-0-0_create_students_table.php
Edit the migration:
// database/migrations/xxxx_xx_xx_create_students_table.php
public function up(): void
{
Schema::create('students', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string('name');
$table->string('email')->unique();
$table->string('phone');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
Run the migration:
php artisan migrateStep 4 Create Controller for Students
php artisan make:controller StudentController -rThis creates app/Http/Controllers/StudentController.php with all 7 resource methods.
- Index // display list of students
- Create // provide call form students from views
- Edit // provide form to the users
- Store // send data to the database
- Update // update data by checking user inputs
- Destroy // deleting data from database based on customer provide form
- Show // showing detail of students by id viewers hits.
Step 5 Define Routes
Open routes/web.php and add:
use App\Http\Controllers\StudentController;
Route::get('/', function () {
return redirect()->route('students.index');
});
Route::resource('students', StudentController::class);
This will create all CRUD routes:
| Method | URL | Action |
| GET | /students | index (list) |
| GET | /students/create | create form |
| POST | /students | store (save new) |
| GET | /students/{id}/edit | edit form |
| PUT | /students/{id} | update |
| DELETE | /students/{id} | destroy |
Step 6 Implement Controller Logic
Edit app/Http/Controllers/StudentController.php:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Models\Student;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class StudentController extends Controller
{
// Show all students
public function index()
{
$students = Student::all();
return view('students.index', compact('students'));
}
// Show create form
public function create()
{
return view('students.create');
}
// Save new student
public function store(Request $request)
{
$request->validate([
'name'=>'required',
'email'=>'required|email|unique:students',
'phone'=>'required'
]);
Student::create($request->all());
return redirect()->route('students.index')->with('success','Student created successfully.');
}
// Show edit form
public function edit(Student $student)
{
return view('students.edit', compact('student'));
}
// Update student
public function update(Request $request, Student $student)
{
$request->validate([
'name'=>'required',
'email'=>'required|email|unique:students,email,'.$student->id,
'phone'=>'required'
]);
$student->update($request->all());
return redirect()->route('students.index')->with('success','Student updated successfully.');
}
// Delete student
public function destroy(Student $student)
{
$student->delete();
return redirect()->route('students.index')->with('success','Student deleted successfully.');
}
}
Also update the model to allow mass assignment:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Student extends Model
{
//
protected $fillable = ['name','email','phone'];
}
Step 7 — Create Blade Views
Make a folder resources/views/students.
resources/views/layout.blade.php
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Student CRUD</title>
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.3/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container mt-5">
<h2 class="mb-4 text-center">Student Management</h2>
@if(session('success'))
<div class="alert alert-success">{{ session('success') }}</div>
@endif
@yield('content')
</div>
</body>
</html>
resources/views/students/index.blade.php
@extends('layout')
@section('content')
<a href="{{ route('students.create') }}" class="btn btn-primary mb-3">+ Add Student</a>
<table class="table table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>ID</th><th>Name</th><th>Email</th><th>Phone</th><th>Actions</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@forelse ($students as $student)
<tr>
<td>{{ $student->id }}</td>
<td>{{ $student->name }}</td>
<td>{{ $student->email }}</td>
<td>{{ $student->phone }}</td>
<td>
<a href="{{ route('students.edit',$student->id) }}" class="btn btn-sm btn-warning">Edit</a>
<form action="{{ route('students.destroy',$student->id) }}" method="POST" style="display:inline-block;">
@csrf @method('DELETE')
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-sm btn-danger"
onclick="return confirm('Delete this student?')">Delete</button>
</form>
</td>
</tr>
@empty
<tr><td colspan="5" class="text-center">No students found.</td></tr>
@endforelse
</tbody>
</table>
@endsection
resources/views/students/create.blade.php
@extends('layout')
@section('content')
<form action="{{ route('students.store') }}" method="POST">
@csrf
<div class="mb-3">
<label>Name</label>
<input type="text" name="name" class="form-control" required>
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label>Email</label>
<input type="email" name="email" class="form-control" required>
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label>Phone</label>
<input type="text" name="phone" class="form-control" required>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-success">Save</button>
<a href="{{ route('students.index') }}" class="btn btn-secondary">Back</a>
</form>
@endsection
resources/views/students/edit.blade.php
@extends('layout')
@section('content')
<form action="{{ route('students.update',$student->id) }}" method="POST">
@csrf @method('PUT')
<div class="mb-3">
<label>Name</label>
<input type="text" name="name" value="{{ $student->name }}" class="form-control" required>
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label>Email</label>
<input type="email" name="email" value="{{ $student->email }}" class="form-control" required>
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label>Phone</label>
<input type="text" name="phone" value="{{ $student->phone }}" class="form-control" required>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-success">Update</button>
<a href="{{ route('students.index') }}" class="btn btn-secondary">Back</a>
</form>
@endsection
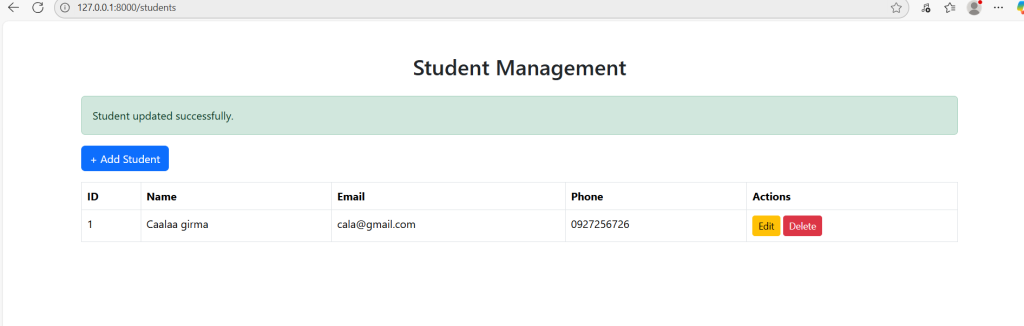
Summary
What You Learned
- How Laravel MVC fits together in a real CRUD system
- How to make migrations, models, controllers, routes, and views
- How to handle forms, validation, and redirects

